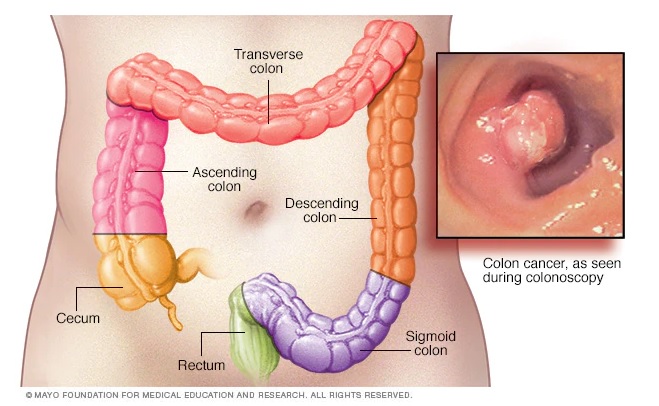
Colon cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the large intestine (colon). The colon is the final part of the digestive tract and is a very common kind of cancer. Colon cancer typically affects older people, it can happen at any age. The positive side is that colon cancer has a very high rate of cure and survival through screening colonoscopies.
Our Human body has large and small intestines. But the colon is located in the top portion of the large intestine, and the anus is located in the lower portion. Colorectal carcinoma is the term used to describe cancer of the large intestine that can extend to both areas. As food is digested, the colon collects water and nutrients. On the other side, the rectum is used to remove waste from the body. The colon is divided into four sections, and cancer can begin to develop in any one of these sections.
In our human body first a polyp will appear, then a colon malignant tumor first appears, which is just a growth of a tissue. If this polyp, not treated timely, then this polyp will expand into the colon and eventually turn cancerous. The basic seed of colon cancer is a particular kind of polyp known as an adenomacan. A polyp typically takes 5 to 10 years to grow to a diameter of about.5 inches. It takes another 5–10 years for this to turn into cancer.
Yes, there are many diagnostic techniques are available to detect any cancerous growth or polyps. Some techniques are colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and biopsy. In addition, patients can undergo screenings to look for polyps or cancerous growths by looking for blood in the stool or an unexplained iron shortage.
Some extensive research is being done to improve the survival rates and promote early detection.
What causes colon Cancer
Doctors are still searching for what causes colon cancers. Generally, colon cancer begins when a healthy cell, experiences DNA abnormalities. The DNA contains a set of instructions that tell a cell what to do.
Many times it has been observed by doctors that when a cell’s DNA is damaged and becomes cancerous, cells continue to divide — even when new cells aren’t needed. As the cells accumulate, they form a tumor.
The cancer cells may spread over time and damage healthy tissue. Additionally, cancerous cells can travel to other parts of the body to form deposits there (metastasis).
What are early symptoms of Colon Cancer
There are many symptoms of colon cancer, you can easily identify especially in the early stages
1.Constipation
A hard, dry bowel movements or passing stool fewer than three times a week.
- Diarrhea
Loose, watery stools and feeling of urgent need to have a bowel movements multiple times in a day.
- Changes in Stool color
Usually it’s dark brown, but If you see any color difference in the stool.(No such specific color)
- Changes in Stool Shape
If you notice any stringy poop, which is also referred as stools that are thin, just like pencil-thin or narrow.
- Blood in Stool
If you notice any blood while passing stool
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Excessive gas
- Abdominal cramps
- Abdominal pain
Some other symptoms can be noticed such as
- Unexplained loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Jaundice
- Anemia
- Weakness
- Fatigue
What is the survival rate of Colon Cancer patients?
The survival rate of colon cancer patients depends on the percentage of people have with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive after they were diagnosed. Those people may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is the treatment will be successful.
What are the types of Colon Cancer
The types of colon cancer are below.
Adenocarcinoma
Majority of Colon cancer is adenocarcinoma. The cells that line inside the surface of colon.
Carcinoid Tumors
It starts in hormone-producing cells in the intestines.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
The colon, gastrointestinal stromal tumors are a form of soft tissue sarcoma that can develop anywhere in the digestive system. These tumors may also be different sarcoma subtypes with vascular or connective tissue origins in the colon.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer which is related to the immune system of the body.
Hereditary Colon Cancer
This cancer is not common only 5 to 10 percent of people get Hereditary colon cancer, because of specific mutations in the genes that are passed from parents to children.
How to Prevent Colon Cancer
Yes, there are 8 ways to prevent colon cancer
- Eat More Grains and Fiber
Eat a diet which is high in fiber and whole grains. This diet will help in reducing the chances of developing colon cancer. Try to have three or more servings of whole grains each day, as well as 22 to 34 grams of fiber, depending on your age and gender.
Increase the quantity of fruits, vegetable and whole-grain food.
2. Reduce Eating Red Meat
The risk of colon cancer is raised by consuming excessive amounts of red meat, such as pork and hamburger. Additionally, danger is increased by processed meats like bacon, sausage, and bologna. Try to limit your weekly intake to three servings.
3. Get Calcium and Vitamin D
Getting enough calcium and vitamin d can help against colon cancer. Try for 1000 to 1200 mg per day of calcium and about 1000 IU per day of vitamin D. Start taking multivitamins and multimineral, but should not take the place of real food or a healthy diet
4. Do Regular Excercise
Do regular physical exercise, Any amount of physical activity is better than none. Start what you like to do such as walking, cycling dancing or even gardening.
5. Quit Smoking
Quit smoing is the best thing you can do for your health. As it causes 15 different cancers including colon cancer. It also increases risk of heart diseases.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Yes, it is also very important to maintain a healthy weight, because obese causes 13 different cancers including colon cancer. So, first goal is to try to stop gaining weight
7. Limited Alcohol Intake
If you are alcoholic then there are high chances of getting colon cancer. Moreover, alcohol can raise the risk of breast cancer.
8. Get Screened
The only strategy to avoid developing colon cancer is to undergo routine screening tests. By identifying abnormal growths called polyps that can develop into cancer.